Disclaimer
How i can get Bitcoin Address from a Bitcoin Private Key. I understand the whole method except the first one where, the public key and its x and y cord comes from the hash/private key. If i can get a code example in php it would be more helpful for me.
This project was written in May 2013 for educational purposes.
Modern cryptocurrency wallets should use hierarchical deterministic (HD) keys instead.
Introduction
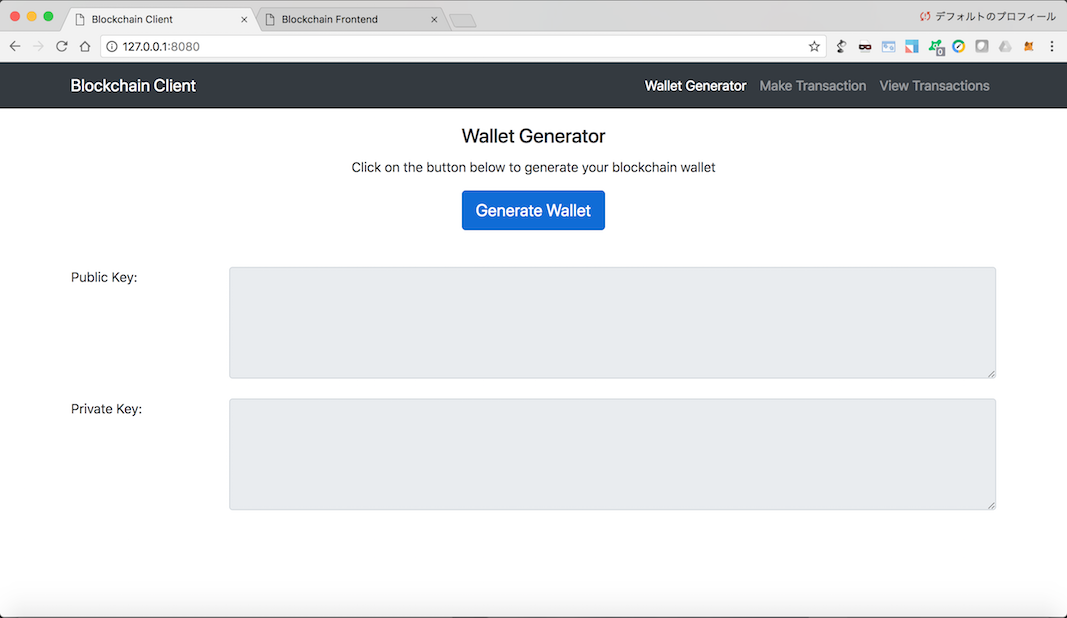
btckeygenie is a standalone Bitcoin keypair/address generator written in Go.btckeygenie generates an ECDSA secp256k1 keypair, dumps the public key incompressed and uncompressed Bitcoin address, hexadecimal, and base64 formats,and dumps the private key in Wallet Import Format (WIF), Wallet Import FormatCompressed (WIFC), hexadecimal, and base64 formats.
btckeygenie includes a lightweight Go package called btckey to easily generatekeypairs, and convert them between compressed and uncompressed varieties ofBitcoin Address, Wallet Import Format, and raw bytes.
See documentation on btckey here: https://godoc.org/github.com/vsergeev/btckeygenie/btckey
Donations are welcome at 15PKyTs3jJ3Nyf3i6R7D9tfGCY1ZbtqWdv :-)
Usage
Generating a new keypair
Importing an existing WIF/WIFC
Help/Usage
Installation
To fetch, build, and install btckeygenie to $GOPATH/bin:
License
btckeygenie is MIT licensed. See the included LICENSE file for more details.
There is more to a bitcoin wallet than just the address itself. It also contains the public and private key for each of your bitcoin addresses. Your bitcoin private key is a randomly generated string (numbers and letters), allowing bitcoins to be spent. A private key is always mathematically related to the bitcoin wallet address, but is impossible to reverse engineer thanks to a strong encryption code base.
If you don’t back up your private key and you lose it, you can no longer access your bitcoin wallet to spend funds.

As mentioned, there is also a public key. This causes some confusion, as some people assume that a bitcoin wallet address and the public key are the same. That is not the case, but they are mathematically related. A bitcoin wallet address is a hashed version of your public key.
Every public key is 256 bits long — sorry, this is mathematical stuff — and the final hash (your wallet address) is 160 bits long. The public key is used to ensure you are the owner of an address that can receive funds. The public key is also mathematically derived from your private key, but using reverse mathematics to derive the private key would take the world’s most powerful supercomputer many trillion years to crack.
Besides these key pairs and a bitcoin wallet address, your bitcoin wallet also stores a separate log of all of your incoming and outgoing transactions. Every transaction linked to your address will be stored by the bitcoin wallet to give users an overview of their spending and receiving habits.
Last but not least, a bitcoin wallet also stores your user preferences. However, these preferences depend on which wallet type you’re using and on which platform. The Bitcoin Core client, for example, has very few preferences to tinker around with, making it less confusing for novice users to get the hang of it.
Your bitcoin wallet generates a “master” file where all of the preceding details are saved. For computer users, that file is called wallet.dat. It’s saved on a Windows machine, for example, in the C:UserYournameDocumentsAppDataRoamingBitcoinfolder. Make sure to create one or multiple backups of this wallet.dat file on other storage devices, such as a USB stick or memory card. The bitcoin wallet software will let you import a wallet.dat file in case your previous file is damaged or lost, restoring your previous settings, including any funds associated with your bitcoin wallet address.
Example Of Bitcoin Public Key
Check out more information on importing private keys and wallet.dat files.